Interpreting China
How climate risk integration is disrupting the Chinese investment landscape

Key takeaways
- Attitudes towards the climate risks faced by Chinese corporates are changing.
- This is part of a broader shift in perspectives among Chinese consumers, business, and investors.
- An active investment approach – born of both deep local knowledge and an ongoing dialogue with relevant Chinese companies – is essential to translate these macro trends into favourable stock picking.
That investors should care about climate risk seems like a statement of the obvious; acceptance of the potential dangers of climate change and the need to accelerate the green transition are now widely accepted among policy makers, financial market participants, and beyond. Indeed, assessing and quantifying the impact of climate risk on individual investments and portfolios is now standard practice across much of the industry, with climate-related reporting and disclosures becoming mandatory in some jurisdictions. Yet, amid an increasing global focus on these issues, many investors in Chinese equity markets have, so far, largely ignored the significance of climate risk, while others have certainly been put off by a perceived unwillingness among Chinese corporates to address these issues. However, this is certainly set to change as the impacts of both global and domestic Chinese regulation, as well as consumer preferences and the possible impact of extreme adverse weather events, are increasingly factored into analyses of the future growth potential of Chinese companies. These changes will lead to an evolution of the Chinese equity landscape, as well as bringing in potential investors who were previously sceptical of attitudes towards these risks in the Chinese market.
Chart 1: Global equity return sensitivity to increase in the climate risk indices
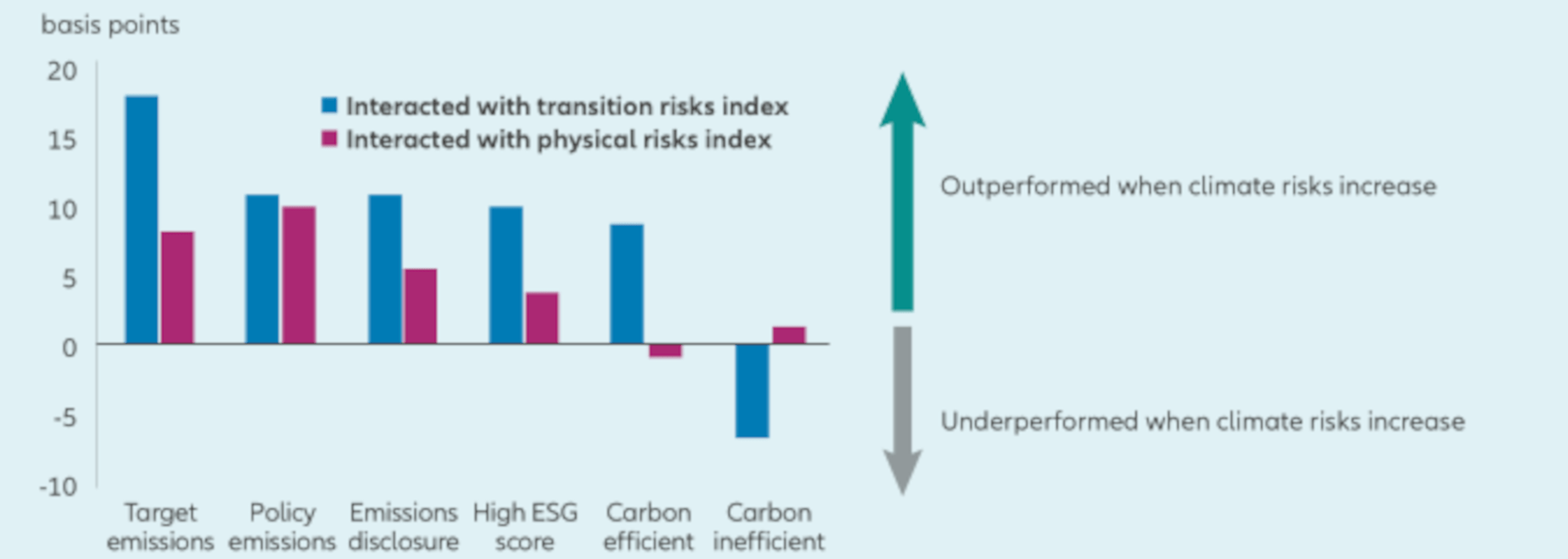
Source: HKMA, Research Memorandum 08/2021, ARE INVESTORS SENSITIVE TO CLIMATE-RELATED TRANSITION AND PHYSICAL RISKS? EVIDENCE FROM GLOBAL STOCK MARKETS. This charts shows global equity’s return sensitivity to changes in climate risk indices. Each pair of blue and purple bars represents equity return sensitivity to increases in the transition and physical risks indices, respectively, for firms in the green/brown categories specified along the x-axis.
Defining climate risk
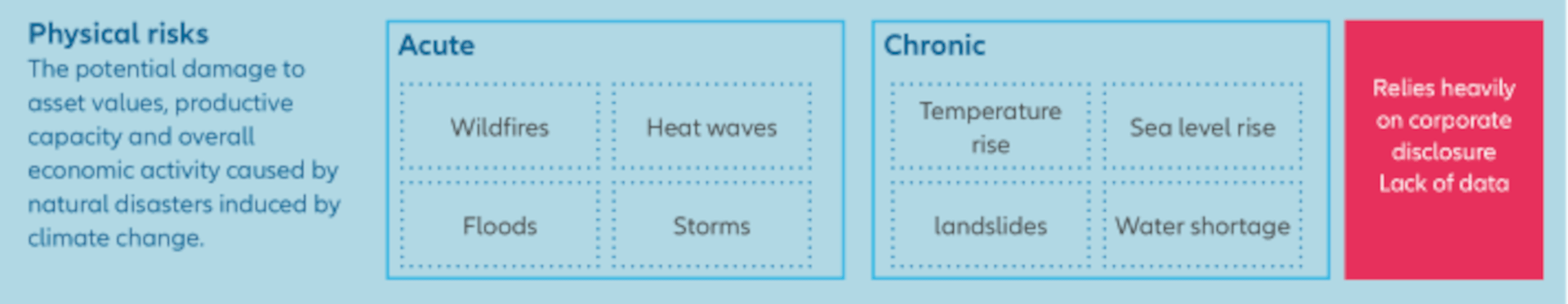
Climate risk can be broken down into two areas: physical risks and transition risks. Physical risks encompass the potential for damage to assets and productive capacity caused by acute climate-related events such as wildfires and floods, as well as the impact of chronic changes such as temperature, water shortages, and sea level rises. Indeed, issues around water present unique challenges for Chinese corporates in several ways. In terms of sea level rises and extreme weather, China’s population and its economic output is focused on densely populated low-elevation and coastal cities, accounting for around 33% of its GDP.1 Furthermore, problems with water scarcity and pollution have long been potential causes of political and economic instability in parts of China, and resolving these issues will be key to China’s ambitions to be a global biodiversity champion.
Whether recent extreme weather or weather-induced events seen across the globe – such as wildfires in the US and Australia, and floods in Europe – are linked to climate change or not, climate-related physical risks certainly represent the greatest potential financial hazard for corporates in the short term, and something that perhaps requires particular attention in China. Furthermore, these types of risks can be hard to assess and quantify, and often depend heavily on corporate disclosure of relevant data.
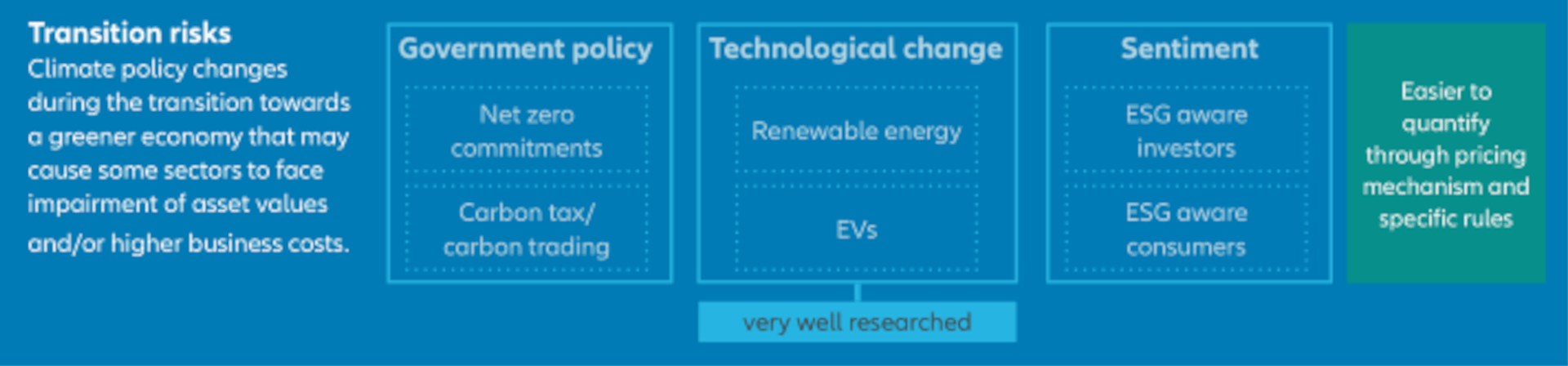
Transition risks, on the other hand, largely stem from the impact of government policy, but also include the effects of both technological development and changing public sentiment on company performance. These types of risks are, in many cases, easier to quantify through rules and mechanisms that allow us to assess potential impacts on asset value and business costs. This relative ease in identifying and quantifying transition risks means that it is these risks that are now receiving the greatest attention are set to be thoroughly integrated into analysts’ and investors’ assessments of Chinese equities.
Factoring in transition risk
For transition risks – both with respect to Chinese companies and beyond – decarbonization is the main theme driving changing regulations, technological developments, and public sentiment towards companies and brands. Looking domestically, China’s “3060” decarbonization plan – the goal of hitting peak carbon dioxide emissions by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060 – encompasses several elements that will impact companies in different sectors to varying degrees depending on their absolute carbon emissions and their intensity of carbon use. For instance, the Chinese national emission trading scheme (ETS) began operating 2021 covering over 2,000 companies in the power sector, and its scope is set to expand to cover further industries. Aside from its expansion to cover more sectors, the aims for the ETS in the coming years include specifying long term carbon reduction targets, building out the necessary legal framework, enhancing corporate carbon data quality and disclosure, and potentially increasing the carbon price. These are all factors that present varying risks – and potential opportunities – to Chinese companies, and the growing impact of the ETS is something that all investors in Chinese equities must now consider.
Climate risks: physical risks and transition risks
Of course, for a country as integrated into global supply chains as China, regulation is not just a domestic issue – a range of other national and transnational legislation focusing on decarbonization and transition will also be hugely impactful on Chinese companies. A good example of the impact of legislation completely outside the purview of Chinese regulators comes with the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). The mechanism is essentially an additional tariff on carbon intensive products imported into the EU and is designed to stem “carbon leakage” from European Union into countries without a carbon price. The legislation will come into force in 2026, with the level of tax ramping up to reach its full value in 2035. While the short-term impact on Chinese corporates is likely to be limited to steel and aluminum manufacturers, this impact is likely to increase if and when the scope of the CBAM is broadened to include non-direct emissions, other carbon intensive industries, and end products that contain carbon intensive materials. Indeed, the CBAM will likely trigger an acceleration of China’s domestic ETS to assist local companies in maintaining their international competitiveness.
A final element of transition risk that must be accounted for is the changing preferences of both investors and end consumers. These changing preferences are leading to a greater proportion of overall investment capital dedicated to ESG investing, and fund outflows from the most carbon intensive areas. However, we are already seeing the most proactive and efficient players – with comprehensive climate disclosures and decarbonization targets – attracting greater flow from investors, and Chinese companies will be no exception to this.
MSCI China Index Constituents - Has the company set targets or objectives to be achieved on emission reduction?
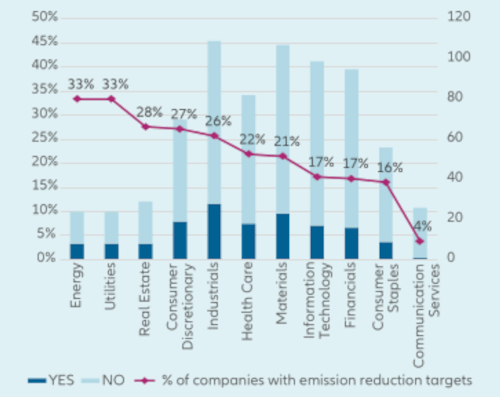
Source: Allianz Global Investors
Changing attitudes
The changes we are now seeing – and that will accelerate in the coming months and years – are indicative of fundamental changes to attitudes towards climate risk in China, and not just in the disclosure and reporting practices of listed companies. This is not just about risk management, but rather about how changing Chinese attitudes are disrupting established ways of doing business in the country. In this respect, we are seeing Chinese consumer expectations evolving in terms of attitudes towards climate and the environment, something reflected in, for example, the drive to clean rivers and achieve better air quality in major cities, as well as in the success of those transition-related industries – such as EVs and solar power – where China is showing leadership.
In this respect, the growing awareness and integration of climate risk by Chinese corporates, financials, and investors is part of a broader sea change that will alter both how business is conducted in China, as well as the attitudes of external partners and investors – potentially opening up investment in domestic Chinese companies to a broader range of investors, especially those that have perhaps previously harboured misgivings around local companies’ commitments to addressing climate change.
Opportunities for investors
While the greater integration of climate risks into assessments of Chinese companies is likely to lead to headwinds for some sectors, in the short term at least, the changing landscape will also present significant opportunities for those taking a nuanced and differentiated approach to investing in Chinese equities.
An active approach to investing in China – that involves a discernment born of both deep local knowledge and an ongoing dialogue with relevant Chinese companies – is thus essential in order to translate the types of macro trends discussed above into identifying an opportunity set and implementing favourable stock picking.







